What is Crawling in Website and Why It's Crucial for Success
Introduction,
What is crawling in Website. There are billions of competing websites for users’ focus on the internet, resulting in a huge environment. However, how do these pages stand up discovered, and indexed by search engines like Google, Bing, and Yahoo? Internet crawling is a vital procedure that holds the key to the solution. The concept of crawling will be talked about in this article, in further to how its roles, why it’s essential for search engine optimization (SEO), and how to ensure your website is efficiently crawled.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat is Crawling in Website?
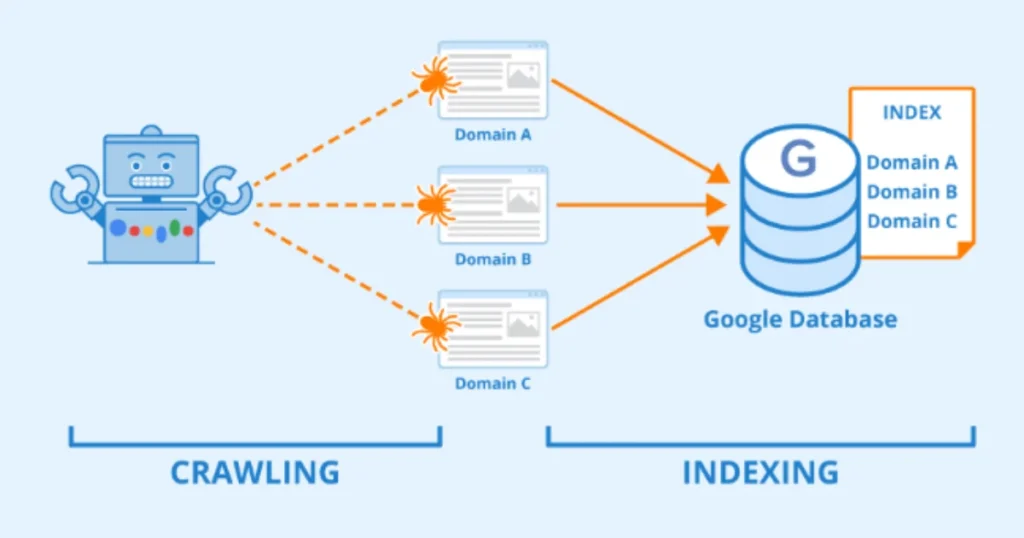
The technique by which search engine bots, sometimes referred to as crawlers or spiders, methodically search the web to locate and gather details on websites is known as crawling. These crawlers index the pages they reveal, follow links, and examine the content to make them searchable by people.
Key Points:
- Crawling is the first step in the search engine’s process of organizing and ranking content.
- Search engines use specialized software like Googlebot to perform crawling.
- Not all pages on the web are crawled; the process depends on various factors such as website quality and structure.
How Does Website Crawling Work?
The crawling process involves several steps:
- Starting with a Known URL:
- Crawlers begin with a list of URLs, often from previous crawls or sitemaps submitted by webmasters.
- Following Links:
- Crawlers navigate through the website by following internal and external links.
- Analyzing Content:
- They examine the page’s content, metadata, and structure.
- Storing Data:
- The gathered data is stored in the search engine’s index for subsequent retrieval throughout user searches.
Why is Crawling Important for SEO?
Crawling is required for search engines to find and assign a ranking your content. If your website isn’t crawled, it will not show up in search results, no matter how worth preserving the content may be.
Key Benefits of Effective Crawling:
- Improved Visibility: Ensures your website is discoverable by search engines.
- Accurate Indexing: Helps search engines understand your content for better ranking.
- Faster Updates: Ensures that modifications to your website are mirrored in search results quickly.
Factors That Impact Crawling
- Website Structure:
- A well-organized site with clear navigation makes it easier for crawlers to find pages.
- Sitemap Submission:
- XML sitemaps guide crawlers to important pages on your site.
- Robots.txt File:
- This file specifies which parts of your site should or should not be crawled.
- Crawl Budget:
- The number of pages a crawler will visit during a session. Larger or frequently updated sites may require optimized crawling strategies.
- Page Speed:
- Faster-loading pages are easier to crawl and improve user experience.
- Backlinks:
- Links from authoritative sites increase the likelihood of crawlers discovering your pages.
How to Boost Your Website for Crawling
- Submit a Sitemap:
- Use Google Search Console or similar tools to upload an XML sitemap.
- Optimize Robots.txt:
- Ensure the file doesn’t block important pages from being crawled.
- Use Internal Linking:
- Link to important pages within your site to help crawlers navigate effectively.
- Avoid Duplicate Content:
- Reduce redundant pages to optimize your crawl budget.
- Fix Broken Links:
- Regularly check and repair broken links to prevent crawler issues.
- Ensure Mobile-Friendliness:
- With mobile-first indexing, having a responsive design is critical.
Common Crawling Issues and Solutions
Common Crawling Issues and Solutions
- Blocked Pages:
- Problem: Important pages blocked in the robots.txt file or via meta tags.
- Solution: Review and update blocking directives.
- Slow Loading Times:
- Problem: Crawlers may skip slow-loading pages.
- Solution: Optimize page speed using tools like Google PageSpeed Insights.
- Orphan Pages:
- Problem: Pages with no internal links may not be discovered.
- Solution: Include these pages in your sitemap or add internal links.
- Exceeding Crawl Budget:
- Problem: Crawlers stop before indexing all pages.
- Solution: Prioritize high-value pages and remove unnecessary ones.
What Makes Indexing Different from Crawling?
During crawling and indexing are closely connected, they are different processes:
- Crawling: The discovery of pages by search engine bots.
- Indexing: The keeping things organized and on of crawled content in a searchable database.
A page must initially be crawled prior to it being able to be indexed and show up in search results.
Tools for Tracking and Enhancing Crawling
- Google Search Console:
- Check crawl stats, submit sitemaps, and identify crawl errors.
- Screaming Frog SEO Spider:
- Examine your site’s framework and determine issues like broken links.
- Ahrefs and SEMrush:
- Offer insights into crawl performance and overall, SEO health.
Future Trends in Website Crawling
- AI-Driven Crawlers:
- Advanced algorithms will enable smarter and faster content discovery.
- Focus on Structured Data:
- Crawlers will increasingly rely on schema markup for better content understanding.
- Enhanced Mobile Crawling:
- As mobile usage grows, crawlers will prioritize mobile-optimized content.
Final Thought, What is Crawling in Website
What is crawling in Website. Search engine optimization is based on website crawling. Regardless of the caliber of its material, your website can not be visible to search engines if crawling isn’t done well. You can guarantee a robust online presence and increase the visibility of your website by comprehending how crawling operates and putting best practices into effect.
Optimizing your website for crawling is an investment in its long-term success, regardless of your role as a webmaster, digital marketer, or company owner. Take charge of the crawling process for your website now, and see the results of your SEO work.
FAQs
The importance of the page, the freshness of the material, and the quantity of internal and external links connecting to the page are some of the characteristics that search engines use to rank crawls.
Indeed, too much crawling, particularly by several bots, can use up server resources and cause your website to load more slowly. Crawl rate management is crucial for this reason.
While shallow crawling concentrates on often updated or high-priority pages, deep crawling examines every page of a website, including those that are rarely updated.
A website’s update frequency, authority, and crawl budget are some of the variables that affect how frequently it is crawled. More people crawl dynamic, high-traffic websites than static ones.
Even though dynamic material and JavaScript can be processed by modern crawlers like Googlebot, poorly written scripts can still impede scanning and indexing.
Avoiding duplicating material, restoring broken links, updating sitemaps frequently, and maintaining short, clean URLs are all examples of best practices.



**herpafend official**
Herpafend is a natural wellness formula developed for individuals experiencing symptoms related to the herpes simplex virus. It is designed to help reduce the intensity and frequency of flare-ups while supporting the bodys immune defenses.
**men balance**
MEN Balance Pro is a high-quality dietary supplement developed with research-informed support to help men maintain healthy prostate function.
I don’t think the title of your article matches the content lol. Just kidding, mainly because I had some doubts after reading the article.