What is VLAN and Why It’s Essential for Secure Networking
Introduction, What is VLAN
What is VLAN. Things to think about, for example, effectiveness, security, and expansion are essential in computer networking. One technical progress that has entirely changed network administration is the Virtual Local Area Network (VLAN). Network engineers may logically partition and manage networks using VLANs without requiring additional physical hardware.
Table of Contents
ToggleTo show you how VLANs might alter the architecture of your network, this lesson examines VLAN kinds, benefits, and real-world applications.
What is VLAN?
Logical segments of a physical network are called VLANs. It enables devices on different parts of the network to communicate as if they were on the same local area network (LAN), any way of their actual places. Rather, than changing hardware, network switch software setups are used to create VLANs.
Key Features:
- Segmentation of networks into logical groups.
- Enhanced control over traffic flow.
- Reduced broadcast domain size.
How VLANs Work
VLANs function by recognizing ethernet frames with recognizers that identify the traffic apart of different VLANs. This method is controlled by the IEEE 802.1Q standard, the most generally used VLAN tagging protocol.
Steps in VLAN Operation:
- VLAN Tagging: Packets are tagged by network switches with VLAN IDs to ensure they are sent to the appropriate VLAN.
- Traffic Segregation: Traffic within a VLAN stays away from other VLANs unless specifically permitted by routing.
- Interaction Among VLANs: Inter-VLAN It is necessary to communicate a router or Layer 3 switch.
Types of VLANs
- Data VLAN:
- Dedicated to carrying user-generated data.
- Example: Office workstations communicating over a specific VLAN.
- Voice VLAN:
- Optimized for Voice over IP (VoIP) traffic.
- Provides priority and low latency for voice data.
- Management VLAN:
- Reserved for network management traffic like switch configurations.
- Enhances security by isolating management interfaces.
- Default VLAN:
- All ports on a switch are initially part of the default VLAN, typically VLAN 1.
- It’s recommended to avoid using the default VLAN for security reasons.
- Native VLAN:
- Used for untagged traffic in 802.1Q implementations.
Benefits of VLANs
- Improved Security:
- By isolating sensitive traffic, VLANs reduce the risk of unauthorized access.
- Efficient Use of Resources:
- VLANs reduce the need for additional physical hardware, such as switches and cables.
- Enhanced Network Performance:
- Minimize broadcast storms by limiting broadcast domains to specific VLANs.
- Simplified Network Management:
- Logical segmentation allows for easier monitoring and troubleshooting.
- Flexibility and Scalability:
- VLANs enable seamless expansion and reconfiguration of networks without physical changes.
VLAN Applications
- Enterprise Networks:
- Segment departments like HR, IT, and Finance to enhance security and manageability.
- Educational Institutions:
- Separate student, faculty, and administrative networks.
- VoIP Implementation:
- Use voice VLANs to prioritize and manage VoIP traffic efficiently.
- Data Centers:
- Isolate different tenant or application traffic within a shared physical infrastructure.
Setting Up VLANs: A Comprehensive Guide
- Access the Switch Interface:
- Log into the switch using its management interface (web, CLI, or GUI).
- Create a VLAN:
- Create a new VLAN by distributing it a unique ID (e.g., VLAN 10).
bash
Copy code
Switch config# vlan 10
Switch config-vlan# name Sales
- Assign Ports to the VLAN:
- Designate specific ports for VLAN membership.
bash
Copy code
Switch(config)# interface fastethernet 0/1
Switch(config-if)# switchport access vlan 10
- Verify VLAN Configuration:
- Use commands like show vlan to review the setup.
bash
Copy code
Switch# show vlan brief
Challenges and Limitations of VLANs
- Complexity in Large Networks:
- Managing multiple VLANs across numerous switches can be challenging.
- Inter-VLAN Communication:
- Requires additional configuration and hardware, such as Layer 3 switches.
- Potential Misconfigurations:
- Misconfigured VLANs can lead to security breaches or connectivity issues.
- Performance Overhead:
- VLAN tagging adds slight processing overhead.
Best Practices for VLAN Implementation
- Plan Your VLAN Strategy:
- Map out VLANs based on organizational requirements and traffic types.
- Use Secure VLAN Management:
- Restrict access to VLAN management interfaces.
- Avoid VLAN 1:
- Reduce security risks by not using the default VLAN for critical traffic.
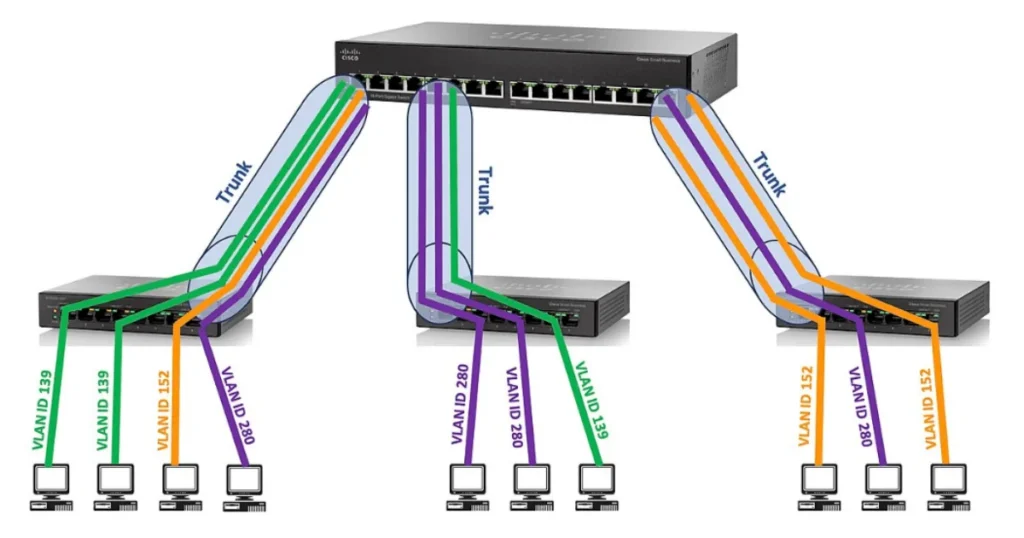
- Implement VLAN Trunking:
- Use trunk links to allow multiple VLAN traffic between switches.
- Monitor VLAN Performance:
- Regularly review VLAN configurations and traffic patterns for optimization.
Future of VLAN Technology
- Integration with SDN:
- Software-Defined Networking (SDN) enhances VLAN flexibility by centralizing control.
- Hybrid Network Models:
- VLANs will increasingly coexist with virtualized network functions like VXLANs.
- Improved Automation Tools:
- Automation will make things easier for VLAN development, management, and debugging.
In Conclusion
What is VLAN. A key component of contemporary network architecture, VLANs allow for logical segmentation, enhanced security, and effective resource use. The performance and scalability of your network can be greatly improved by comprehending and utilizing VLANs, regardless of whether you’re in charge of a small business network or a large enterprise architecture.
You may fully utilize VLANs to create a reliable and future-ready network by adhering to best practices and keeping up with developments.
FAQs
It is possible to use VLANs in wireless networks to divide up traffic, usually by giving each SSID (wireless network name) a unique VLAN.
VLAN hopping is a kind of network attack in which a malevolent user enters another VLAN without authorization. By turning off unnecessary ports, turning on VLAN tagging, and putting secure trunk configurations in place, it can be avoided.
Traffic leaving and re-entering a VLAN on distinct paths results in asymmetrical routing, which can lead to problems like packet loss. Routing setups that are consistent can help prevent it.
It is possible to separate virtual computers, services, and data traffic in cloud infrastructures using VLANs, which guarantees security and effective administration.
In dynamic environments like data centers, where traffic is split up across several VLANs for load balancing and scalability, a VLAN pool is a collection of VLANs.
Indeed, by limiting faults to particular network segments, VLANs facilitate troubleshooting and enable speedier problem identification and resolution.



buy cannabis legally online worldwide